研究室工作进展 Nov. 17th, 2016
Structure and Reaction Chemistry of Magnesium Organocuprates
Derived from Magnesiacyclopentadienes and Copper(I) Salts
Liang Liu, Junnian Wei, Yue Chi, Wen-Xiong Zhang*, and Zhenfeng Xi*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14762-14765.
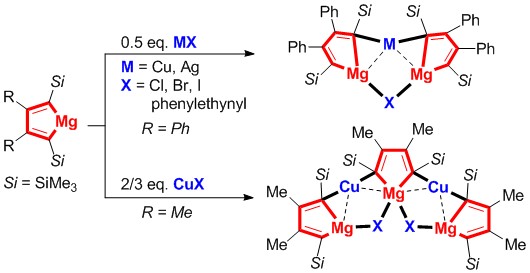
Organocopper(I) compounds are ubiquitously involved in Cu-based reactions as synthetic reagents or key intermediates. Among them, lithium organocuprates have been widely applied in synthetic chemistry. Many lithium organocuprates have been structurally characterized. However, in sharp contrast, magnesium organocuprates, particularly in terms of their well-defined structures, remain almost unexplored, although different structural characteristics and useful reaction chemistry can be expected.
Chemistry of magnesium organocuprates, including their synthesis, structures, and reactions, remains rarely explored. In this work, by taking advantage of the high reactivity and ready availability of magnesiacyclopentadienes, a series of magnesiacyclopentadiene-based organocuprates were synthesized and structurally characterized. A variety of CuX salts, in which X was Cl, Br, I, and alkynyl, could be successfully applied to react with magnesiacyclopentadienes. Besides CuX salts, AgX (X = Cl, alkynyl) could also undergo the above reaction, affording the corresponding magnesium organoargentate. Single-crystal X-ray structural analysis and DFT calculations of these butadienyl magnesium organocuprates revealed unique structural characteristics and bonding modes, which are also very useful to understand the transmetalation reaction mechanism and its intermediacy between organomagnesium compounds and coinage metal salts. Preliminary reaction chemistry of these magnesium organocuprates have been demonstrated by their reactions with allyl bromide, benzoyl chloride, and CO2.
